 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||
产品简介
产品简介:
| 产品编号 | 产品名称 | 产品包装 | 产品价格 |
| C1038 | DiO(细胞膜绿色荧光探针) | 10mg | 441.00元 |
DiO即DiOC18(3),全称为3,3′-dioctadecyloxacarbocyanine perchlorate,是最常用的细胞膜荧
光探针之一,呈现绿色荧光。DiO是一种亲脂性膜染料,进入细胞膜后可以侧向扩散逐渐使整个细胞的细胞膜被染色。
DiO在进入细胞膜之前荧光非常弱,仅当进入到细胞膜后才可以被激发出很强的荧光。DiO被激发后
可以发出绿色的荧光,DiO和磷酯双层膜结合后的激发光谱和发射光谱参考下图。其中,最大激发波长为484nm,最大发射波长为501nm。
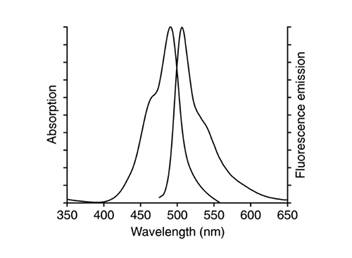
DiO的分子式为C53H85ClN2O6,分子量为881.72,CAS number为34215-57-1。
DiO可以溶解于无水乙醇、DMSO和DMF,溶解度约为1-2.5mg/ml。发现较难溶解时可以适当加热,并
用超声处理以促进溶解。
DiO被广泛用于正向或逆向的,活的或固定的神经等细胞或组织的示踪剂或长期示踪剂(long-term
tracer)。DiO通常不会明显影响细胞的生存力(viability)。DiO对于细胞膜染色的荧光强度通常要低于DiI,有时对于某些经过固定的组织的染色效果欠佳。
DiO除了最简单的细胞膜荧光标记外,还可以用于检测细胞的融合和粘附,检测发育或移植过程中细胞迁移,通过FRAP(Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching)检测脂在细胞膜上的扩散,检测细胞毒性和标记脂蛋白等。
用于细胞膜荧光标记时,DiO的常用浓度为1-30μM,最常用的浓度为5-10μM。DiO可以直接染色活
的细胞或组织,染色时间通常为5-20分钟。对于固定的细胞或组织,通常宜使用配制在PBS中的4%多聚甲醛进行固定,使用其它不适当的固定液会导致荧光背景较高。
包装清单:
产品编号 |
产品名称 |
包装 |
C1038 |
DiO(细胞膜绿色荧光探针) |
10mg |
— |
说明书 |
1份 |
保存条件:
4℃避光保存,一年有效。配制的储存液-20℃避光保存,半年有效。
注意事项:
荧光染料均存在淬灭问题,请尽量注意避光,以减缓荧光淬灭。
为了您的安全和健康,请穿实验服并戴一次性手套操作。
使用说明
使用说明:
产品图片

相关产品
相关论文
使用本产品的文献:
1. Ma Y, Zhuang Y, Xie X, Wang C, Wang F, Zhou D, Zeng J, Cai L.
The role of surface charge density in cationic liposome-promoted dendritic cell
maturation andvaccine-induced immune responses.
Nanoscale. 2011 May;3(5):2307-14.
2. Jiang QY, Lai LH, Shen J, Wang QQ, Xu FJ, Tang GP
Gene delivery to tumor cells by cationic polymeric nanovectors coupled to folic acid and
the cell-penetrating peptide octaarginine.
Biomaterials. 2011 Oct;32(29):7253-62.
3. Shi YY, Wang YS, Zhang ZX, Cai Y, Zhou J, Hou HY, van Rooijen N.
Monocyte/macrophages promote vasculogenesis in choroidal neovascularization in mice
bystimulating SDF-1 expression in RPE cells.
Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011 Nov;249(11):1667-79. Epub 2011 Jun 8.
4. Zhao W, Zhang WP, Zhang ZL, He RL, Lin Y, Xie M, Wang HZ, Pang DW.
Robust and highly sensitive fluorescence approach for point-of-care virus detection
based onimmunomagnetic separation.
Anal Chem. 2012 Mar 6;84(5):2358-65. doi: 10.1021/ac203102u. Epub 2012 Feb 16.
5. Xiong XY, Guo L, Gong YC, Li ZL, Li YP, Liu ZY, Zhou M
In vitro &in vivo targeting behaviors of biotinylated Pluronic F127/poly(lactic acid)
nanoparticlesthrough biotin-avidin interaction.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012 Aug 15;46(5):537-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2012.04.011.
Epub 2012 Apr 16.
6. Zhang Z, Xiong X, Wan J, Xiao L, Gan L, Feng Y, Xu H, Yang X.
Cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of PEG-b-PLA polymeric micelles.
Biomaterials. 2012 Oct;33(29):7233-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.06.045.
Epub 2012 Jul 15.
7. Zhang W, Dang S, Hong T, Tang J, Fan J, Bu D, Sun Y, Wang Z, Wisniewski T.
A humanized single-chain antibody against beta 3 integrin inhibits pulmonary
metastasis by preferentially fragmenting activated platelets in the tumor
microenvironment.
Blood. 2012 Oct 4;120(14):2889-98. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-425207. Epub 2012 Aug 9.
8. Zhuang Y, Ma Y, Wang C, Hai L, Yan C, Zhang Y, Liu F, Cai L.
PEGylated cationic liposomes robustly augment vaccine-induced immune responses: Role of
lymphatictrafficking and biodistribution.
J Control Release. 2012 Apr 10;159(1):135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.12.017.
Epub 2011 Dec 29.
9. Wu Y, Feng W, Zhang H, Li S, Wang D, Pan X, Hu S.
Ca2+-regulatory proteins in cardiomyocytes from the right ventricle in children with
congenital heart disease.
J Transl Med. 2012 Apr 2;10:67. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-67.
10.Wang ZG, Liu SL, Tian ZQ, Zhang ZL, Tang HW, Pang DW.
Myosin-driven intercellular transportation of wheat germ agglutinin mediated by membrane
nanotubes betweenhuman lung cancer cells.
ACS Nano. 2012 Nov 27;6(11):10033-41. doi: 10.1021/nn303729r. Epub 2012 Nov 1.
11. Song W, Wu K, Yan J, Zhang Y, Zhao L.
MiR-148b laden titanium implant promoting osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells.
RSC Adv., 2013, Advance Article.
12.Li P, Gao Y, Zhang J, Liu Z, Tan K, Hua X, Gong J.
Renal interstitial permeability changes induced by microbubble-enhanced diagnostic
ultrasound.
J Drug Target. 2013 May;21(5):507-14. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2013.776053.
Epub 2013 Apr 29.
13.Luo J, Zhao X, Tan Z, Su Z, Meng F, Zhang M.
Mesenchymal-like progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells promote recovery
from acute kidneyinjury via paracrine actions.
Cytotherapy. 2013 Jun;15(6):649-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Feb 14.
14.Wu K, Xu J, Liu M, Song W, Yan J, Gao S, Zhao L, Zhang Y.
Induction of osteogenic differentiation of stem cells via a lyophilized microRNA reverse
transfection formulationon a tissue culture plate.
Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1595-607. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S43244. Epub 2013 May 3.
15.Zhang B, Luo Z, Liu J, Ding X, Li J, Cai K.
Cytochrome c end-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as redox-responsive drug
delivery vehicles for liver tumor-targeted triplex therapy in vitro and in vivo.
J Control Release. 2014 Oct 28;192:192-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.06.037. Epub
2014 Jul 15.
16.He M, Wang Z, Cao Y, Zhao Y, Duan B, Chen Y, Xu M, Zhang L.
Construction of Chitin/PVA Composite Hydrogels with Jellyfish Gel-Like Structure and
Their Biocompatibility.
Biomacromolecules. 2014 Sep 8;15(9):3358-65. doi: 10.1021/bm500827q. Epub 2014 Aug 8.
17.Wang W, Yuan C, Wang S, Song X, Xu L, Yan R, Hasson IA, Li X.
Transcriptional and proteomic analysis reveal recombinant galectins of Haemonchus
contortus down-regulated functions of goat PBMC and modulation of several signaling
cascades in vitro.
J Proteomics. 2014 Feb 26;98:123-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.12.017. Epub 2014 Jan
5.
18.He M, Zhao Y, Duan J, Wang Z, Chen Y, Zhang L.
Fast contact of solid-liquid interface created high strength multi-layered cellulose
hydrogels with controllable size.
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014 Feb 12;6(3):1872-8. doi: 10.1021/am404855q. Epub
2014 Jan 17.
苏ICP备06009238号 |

